From the Runic to the Latin Alphabet
ᚻᛖᚱᚠᛖᚷᛏᚪᚦᛏᛁᛏᚢᛋᛖᚾᛞᚷᛁᚢᚦᛖᚪᛋᚢ - Here fight Titus and the Jews.

Key words
- Remnant: a small piece or amount of something that is left from a larger original piece or amount
The dog ate the remnants of last night's meal.
- Resurgence: a new increase of activity or interest in a particular subject or idea that had been forgotten for some time
There has been a resurgence of interest in Bitcoin.
- Influx: the fact of a large number of people or things arriving at the same time
They are expecting an influx of several thousand refugees over the next few days.
- Revival: the process of becoming more active or popular again
The May Day festival originally celebrated the revival of life in early spring after winter.
- Advent:the fact of an event happening, an invention being made, or a person arriving
Life was transformed by the advent of the steam engine.
Read the article to find the answers
- Who used the Runic alphabet?
- What is "Æ"?
- What caused the influx of Greek vocabulary?
- What accelerated the spread of Latin?
The Runic Alphabet
The Runic alphabet was used by Germanic tribes, including the Anglo-Saxons. Each rune represented a sound and often had a symbolic meaning. Written mainly on wood, stone or metal, runes were used for both communication and magic. Although the Latin alphabet gradually replaced runes with the spread of Christianity, remnants of the Runic system are still in use, and several modern systems of runic magic have been published since the 1980's.
Æ
King Æthelberht's name is still spelt with the rune "Æ" or "ash", which was used in Old English to represent the sound "ah". While its use declined over time, it experienced a resurgence with the increased interest in Ancient Greek, as seen in words such as 'encyclopaedia' and 'aesthetic'. This influx of Greek vocabulary was due to the revival of classical Greek language and literature, driven by increased interest in ancient Greek texts such as the Bible, translated by Wycliffe and Tyndale.
From Runic to Latin
The transition from the runic alphabet to the Latin alphabet in English developed gradually with the rise of Christianity and Latin-speaking missionaries. The spread of Latin accelerated in the 7th century with the establishment of monasteries where monks produced and copied Latin texts.
The Norman Conquest in 1066 consolidated the importance of the Latin script, and by the Middle English period the Latin alphabet had largely replaced the Runic alphabet, a shift that was accelerated by the advent of the printing press in the 15th century.
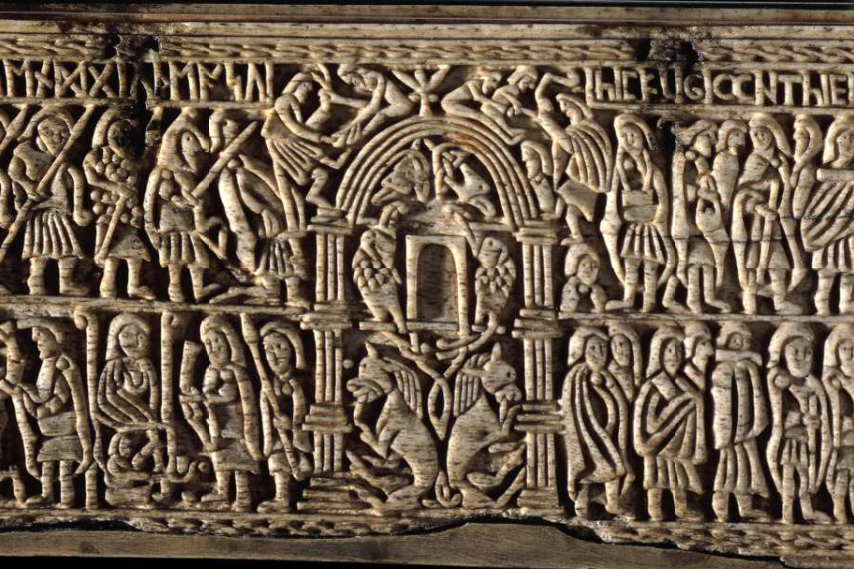
The Franks Casket
The Franks Casket is a small Anglo-Saxon coffin in the British Museum. It is decorated with carved inscriptions, mostly in Anglo-Saxon runes. The back panel, pictured above, depicts the siege of Jerusalem in 70 AD by the Roman general Titus, with a mixture of runic and Latin script inscriptions, illustrating the transition from runic to Latin script.Old English - A mixture of Runic & Latin Scripts
ᚻᛖᚱᚠᛖᚷᛏᚪᚦ
ᛏᛁᛏᚢᛋᛖᚾᛞᚷᛁᚢᚦᛖᚪᛋᚢ
HICFUGIANTHIERUSALIM
Translates to:
Modern English - Latin Script
Here fight Titus and the Jews.
Here the inhabitants flee from Jerusalem.
Discussion questions
- Do you have any questions about any of the vocabulary or grammar in this article?
- How has the script of your mother tongue changed over time?
- Has there ever been a revival of interest in classical literature in your country?
- What ancient carved inscriptions have you seen?

Book a Lesson
Improve your English language communication skills by practicing with a qualified and experienced native speaker.